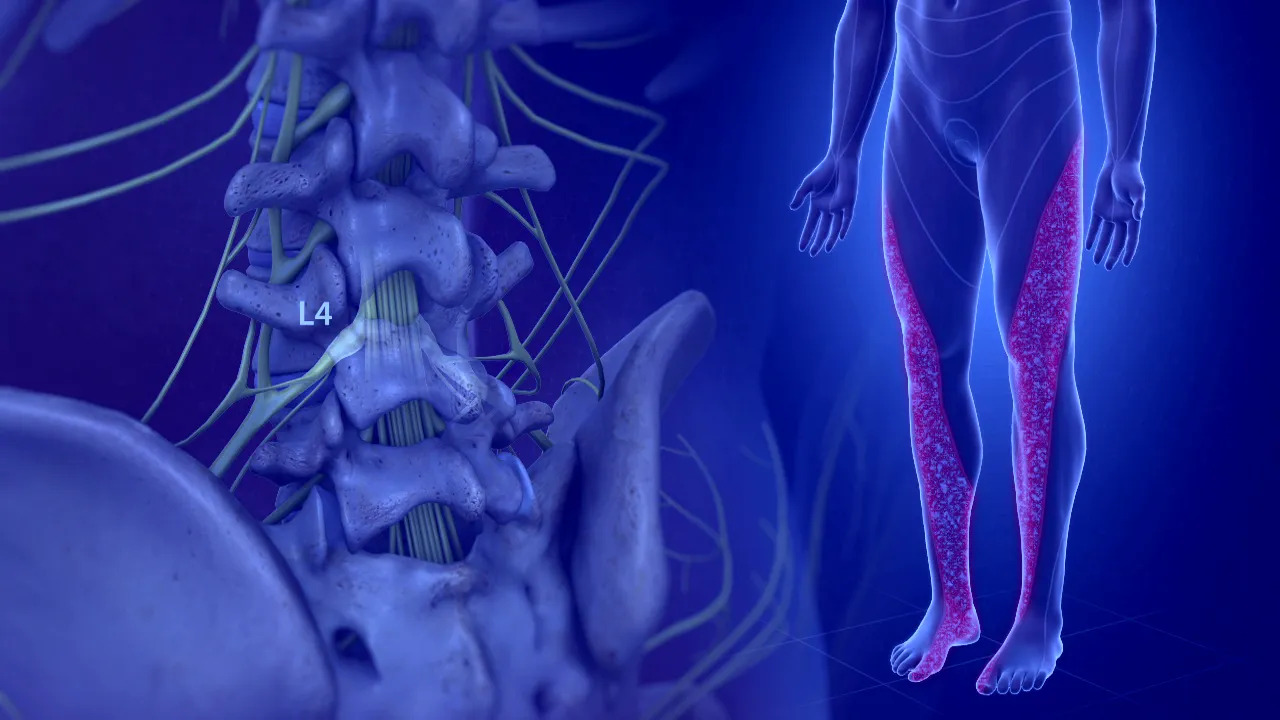
Radiculopathy is a condition that affects the nerves in the spine, causing pain, weakness, and numbness in the arms or legs. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages and can be caused by various factors, including injury, degenerative changes, and compression of the nerves.
• Herniated Discs: A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the disc’s outer layer which can put pressure on the nerves in the spine, causing Radiculopathy.
• Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the nerves in the spine and causing Radiculopathy.
• Degenerative Disc Disease: Degenerative disc disease is when the discs in the spine break down over time, causing them to lose their cushioning ability which can put pressure on the nerves in the spine, causing Radiculopathy.
• Spondylolisthesis: Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which one vertebra slips forward over the vertebra below it, which puts pressure on the nerves in the spine, causing Radiculopathy.
• Trauma: Trauma to the spine, such as a car accident or a fall, can cause Radiculopathy.
The symptoms of Radiculopathy can vary depending on the location of the affected nerve. Common symptoms include:
• Pain: Radiculopathy can cause pain that radiates from the spine to the arms or legs. The pain may be sharp, burning, or shooting.
• Numbness: Radiculopathy can cause numbness or tingling in the arms or legs.
• Weakness: Radiculopathy can cause weakness in the arms or legs, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
• Loss of Reflexes: Radiculopathy can cause a loss of reflexes in the affected area.
Physical exams and imaging tests, such as an X-ray, MRI, or CT scan, can help determine the nerve compression’s location and severity.
The treatment of Radiculopathy depends on the underlying cause. Common treatments include:
• Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve pain associated with Radiculopathy. In some cases, stronger pain medications or muscle relaxants are needed.
• Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve strength and flexibility in the affected area, reducing pain and improving mobility.
• Steroid Injections: Steroid injections can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with Radiculopathy.
• Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the affected nerve. Surgery may involve removing a herniated disc or widening the spinal canal.
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of Radiculopathy, specific steps can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition.
• Maintaining a good posture: Poor posture can pressure the spine, increasing the risk of Radiculopathy.
• Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help improve strength and flexibility in the spine, reducing the risk of Radiculopathy.
• Avoiding heavy lifting: Heavy lifting can strain the spine, increasing the risk of Radiculopathy.
• Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of degenerative disc disease, leading to Radiculopathy.
Radiculopathy is a common condition that can cause pain, weakness, and numbness in the arms or legs. Various factors, including injury, degenerative changes, and compression of the nerves, can cause it. Treatment depends on the condition’s underlying cause and may include medications, physical therapy, steroid injections, or surgery. While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of Radiculopathy, maintaining good posture, exercising regularly, avoiding heavy lifting, and quitting smoking can help reduce your risk of developing the condition.
Comments are closed.