Temporal lobe seizures, also known as complex partial seizures, are a type of seizure that originates in the temporal lobe of the brain. These seizures can cause various symptoms, including altered consciousness, memory loss, and emotional changes.
• Brain injury: Traumatic brain injury, stroke, or brain tumors can damage the temporal lobe and trigger seizures.
• Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to temporal lobe seizures.
• Infections: Infections like meningitis or encephalitis can cause inflammation in the brain and trigger seizures.
• Metabolic disorders: Disorders like hypoglycemia or electrolyte imbalances can affect brain function and trigger seizures.
• Drug or alcohol abuse: Substance abuse can damage the brain and trigger seizures.
The symptoms of temporal lobe seizures can vary from person to person, but they typically involve altered consciousness, memory loss, and emotional changes. Some common symptoms of temporal lobe seizures include:
• Altered consciousness: During a seizure, the patient may experience a loss of awareness or consciousness. They may stare blankly, appear confused, or have a dream-like state.
• Memory loss: The patient may have difficulty remembering what happened before or during the seizure. They may also experience a sense of déjà vu or jamais vu.
• Emotional changes: The patient may experience intense emotions like fear, anxiety, or pleasure. They may also exhibit unusual behaviors like laughing or crying.
• Sensory changes: The patient may experience sensory changes like hallucinations, tingling sensations, or detachment from their surroundings.
• Motor symptoms: The patient may exhibit motor symptoms like repetitive movements, lip-smacking, or chewing.
Diagnosing temporal lobe seizures can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions like migraines or anxiety disorders. However, several tests can help diagnose temporal lobe seizures, including:
• Electroencephalogram (EEG): An EEG is a test that measures the electrical activity in the brain. During an EEG, electrodes are placed on the scalp to record brain waves. Abnormal brain waves can indicate a seizure.
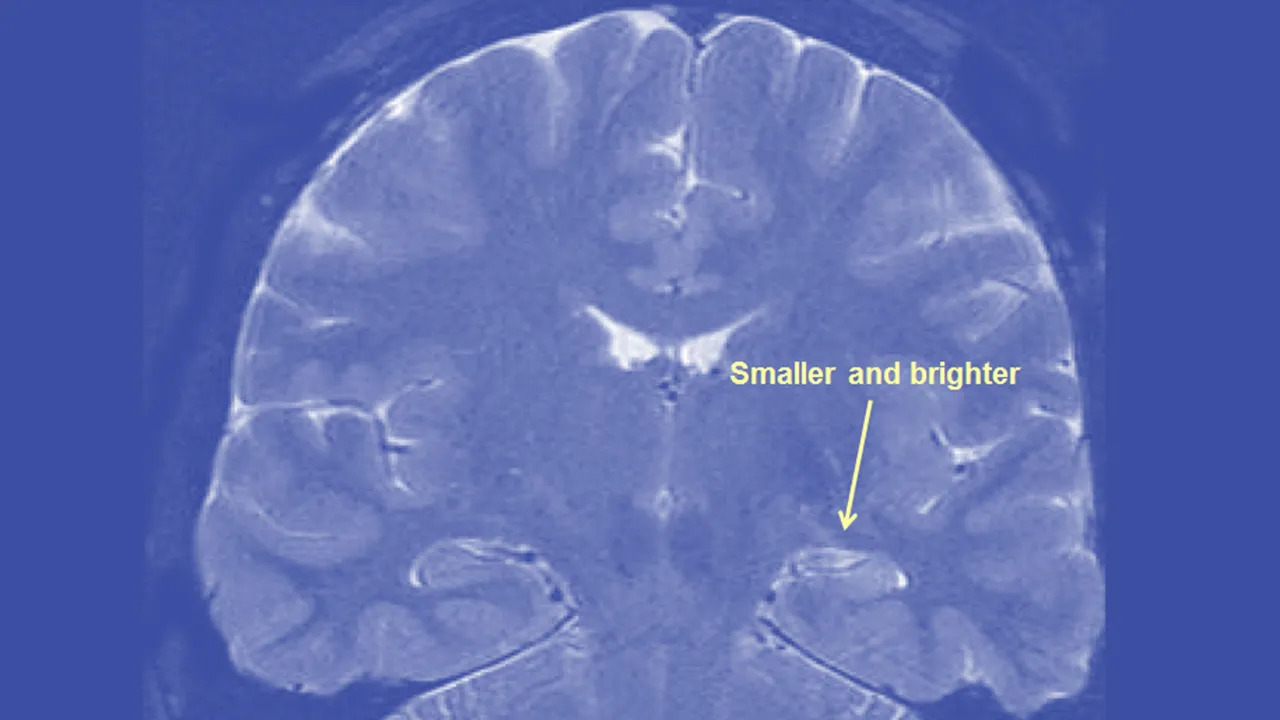
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI is a test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of the brain. An MRI can detect structural abnormalities in the brain that may be causing seizures.
• Video EEG monitoring: Video EEG monitoring involves recording a person’s brain waves and behavior during a seizure, which helps determine the type of seizure and the area of the brain where it originates.
• Neuropsychological testing: Neuropsychological testing can assess a person’s cognitive function, memory, and emotional state, which helps determine the extent of any brain damage caused by seizures.
Treating temporal lobe seizures involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Some common treatments for temporal lobe seizures include:
• Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs): AEDs are medications that can help prevent seizures. Some AEDs used to treat temporal lobe seizures include carbamazepine, phenytoin, and valproic acid.
• Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the part of the brain causing seizures, typically recommended if medication is ineffective or if the seizures are causing significant impairment.
• Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): VNS is a treatment that involves implanting a device that stimulates the vagus nerve in the neck, which helps reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
• Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes like getting enough sleep, reducing stress, and avoiding triggers like alcohol or caffeine can help reduce the frequency of seizures.
Temporal lobe seizures are a type of seizure that originates in the temporal lobe of the brain. These seizures can cause various symptoms, including altered consciousness, memory loss, and emotional changes. The causes of temporal lobe seizures can vary but are often related to brain injury, genetics, infections, or metabolic disorders. Diagnosing temporal lobe seizures can be challenging, but tests like EEG, MRI, and video EEG monitoring can help. Treatment typically involves medication and lifestyle changes, but surgery or VNS may sometimes be recommended. However, with proper treatment, many people with temporal lobe seizures can lead normal, healthy lives.
Comments are closed.