29
Subdural Hematoma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction:
Subdural hematoma is a medical condition that occurs when blood accumulates between the brain and the dura mater, which is the brain’s outermost layer. This condition can be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Causes of Subdural Hematoma:
Various factors, including head injuries, can cause subdural hematoma, falls, and other types of traumas. In some cases, the condition may develop spontaneously without any apparent cause. In addition, the risk of developing subdural hematoma increases with age as the brain becomes more vulnerable to injury.
Symptoms of Subdural Hematoma:
The symptoms of subdural hematoma can vary depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, the symptoms may be mild or not immediately apparent. However, in more severe cases, the symptoms can be life-threatening. Some of the common symptoms of subdural hematoma
include:
• Headache
• Confusion
• Dizziness
• Nausea and vomiting
• Seizures
• Loss of consciousness
• Weakness or numbness in the limbs
• Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
• Vision problems
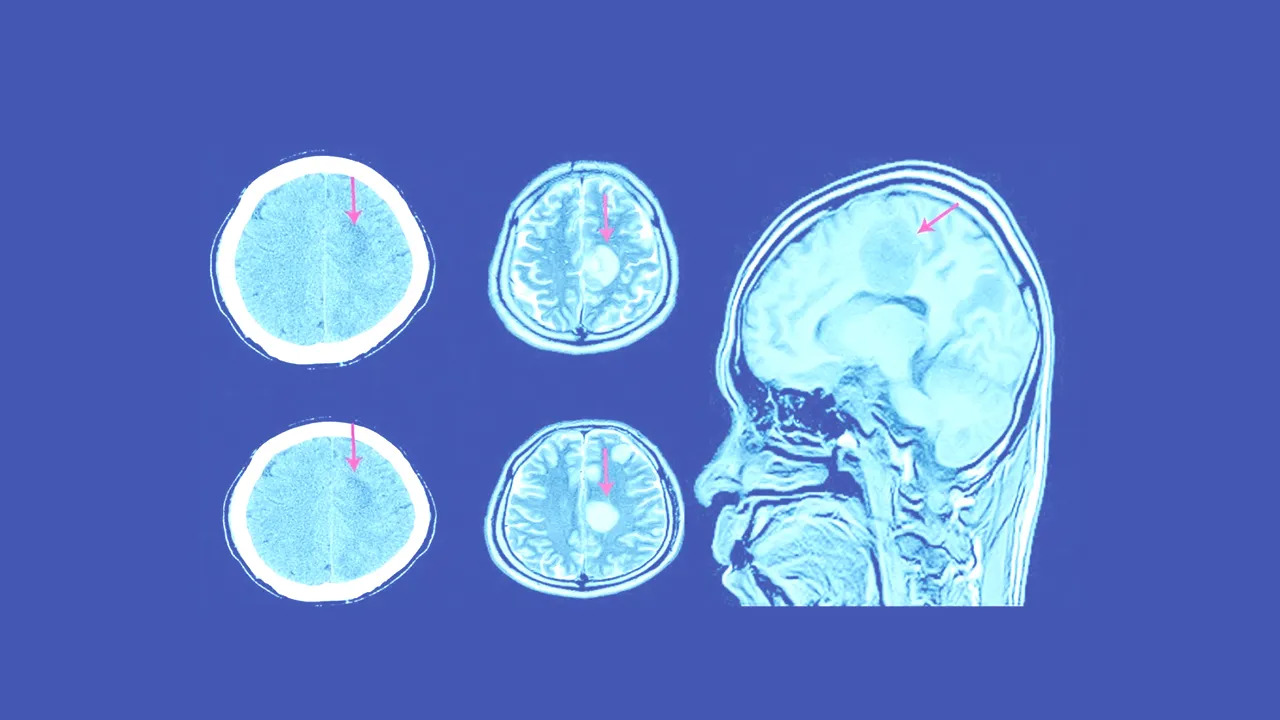
Diagnosis of Subdural Hematoma:
A physical examination and imaging tests, such as a CT or MRI, confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a lumbar puncture may be performed to check for blood in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment of Subdural Hematoma:
The treatment of subdural hematoma depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, the condition may resolve independently without any treatment. However, surgery may be necessary in more severe cases to remove the blood clot and relieve pressure on the brain.
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of subdural hematoma. These may include pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
Prevention of Subdural Hematoma:
It can take several steps to reduce the risk of developing a subdural hematoma. These include:
• Wearing a helmet when participating in high-risk activities, such as cycling, skiing, or skateboarding.
• Using seat belts and child safety seats when driving or riding in a vehicle.
• Taking steps to prevent falls, such as installing handrails and non-slip mats in the bathroom.
• Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, which can increase the risk of falls and other types of traumas.
In Summary:
Subdural hematoma is a serious medical condition that requires prompt treatment. Most people with subdural hematoma can recover fully with proper diagnosis and treatment.



Comments are closed.