
Alcoholic Cerebellar Degeneration (ACD): A Complex Neurological Condition
Introduction Alcoholic cerebellar degeneration (ACD) is a neurological disorder caused by excessive alcohol consumption. It is a type of cerebellar ataxia, a group of disorders that affect the cerebellum. The cerebellum is a small but important part of the brain located at the skull’s base. It is responsible for coordinating movement and balance and regulating […]

Don’t Ignore the Storm: Recognizing and Treating Status Epilepticus (SE)
Introduction Status epilepticus (SE) is a medical emergency characterized by prolonged or repeated back-to-back seizures lasting longer than five minutes, occurring without full recovery of consciousness between seizures, muscle rigidity, convulsions, and breathing difficulties. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention and can occur in people of all ages but is more […]

Understanding Primarily Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures: From Symptoms to Treatment
Primarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures (PGTCS) is a type of seizure that affects the entire brain and can cause seizures presenting with loss of consciousness, convulsions, and muscle rigidity. During the convulsions, the person may experience jerking movements of the arms and legs, bite their tongue, or lose control of their bladder or bowels. After the […]
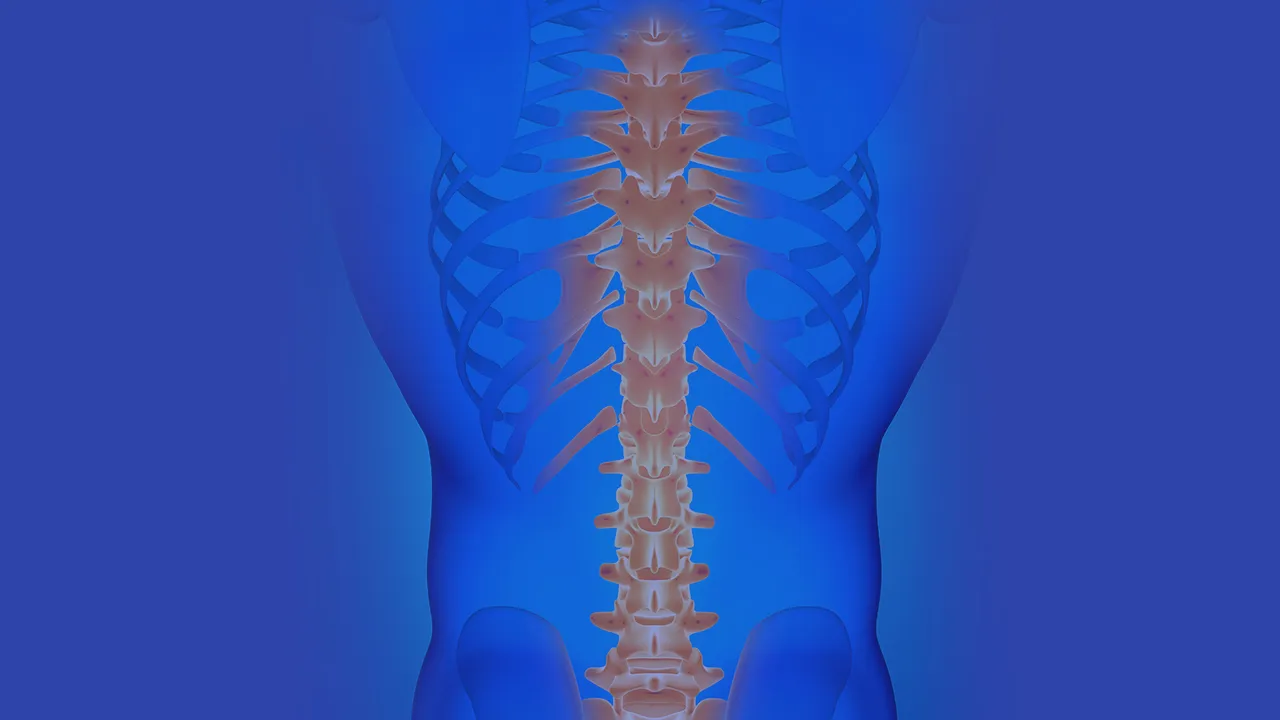
Understanding Transverse Myelitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction Transverse myelitis is a rare neurological condition that affects the spinal cord. It is characterized by inflammation of the spinal cord, which can cause damage to the myelin sheath that surrounds and protects the nerve fibers. This damage can disrupt the normal functioning of the spinal cord, leading to a range of symptoms. Transverse […]
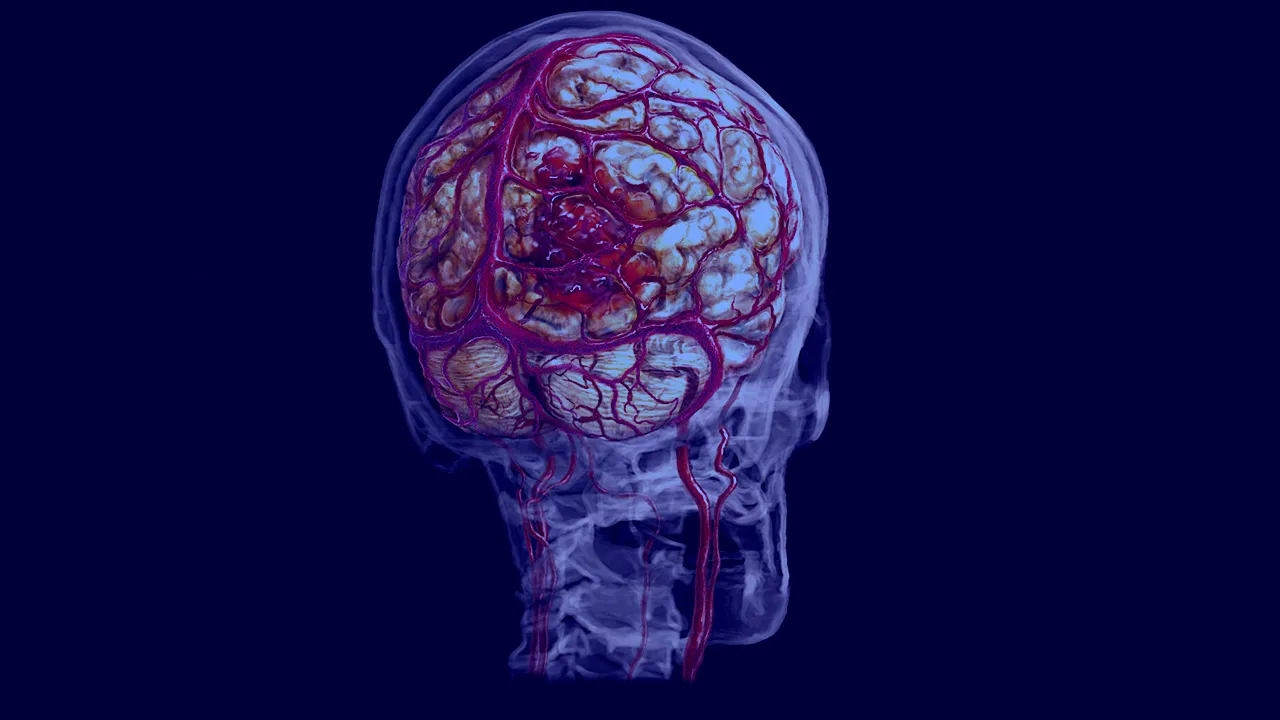
Hemorrhagic Strokes: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention – You need to know
Hemorrhagic Strokes occur when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and bleeds into the surrounding tissue, causing damage to the brain and can be life-threatening. Hemorrhagic strokes account for approximately 15% of all strokes but are responsible for a higher percentage of stroke-related deaths. Types There are two main types of hemorrhagic strokes: Intracerebral […]

Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Unraveling the Mystery of Rapid Muscle Weakness
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare but serious autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It is characterized by the sudden onset of muscle weakness, tingling, and numbness in the limbs, which can rapidly progress to paralysis, difficulty swallowing, speaking, chewing, heart rate, blood pressure changes, and respiratory failure.

Understanding Infantile Spasms: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Infantile spasms, also known as West syndrome, is a rare and severe form of epilepsy that affects infants and young children and is characterized by sudden, brief, and symmetric muscle contractions in clusters.
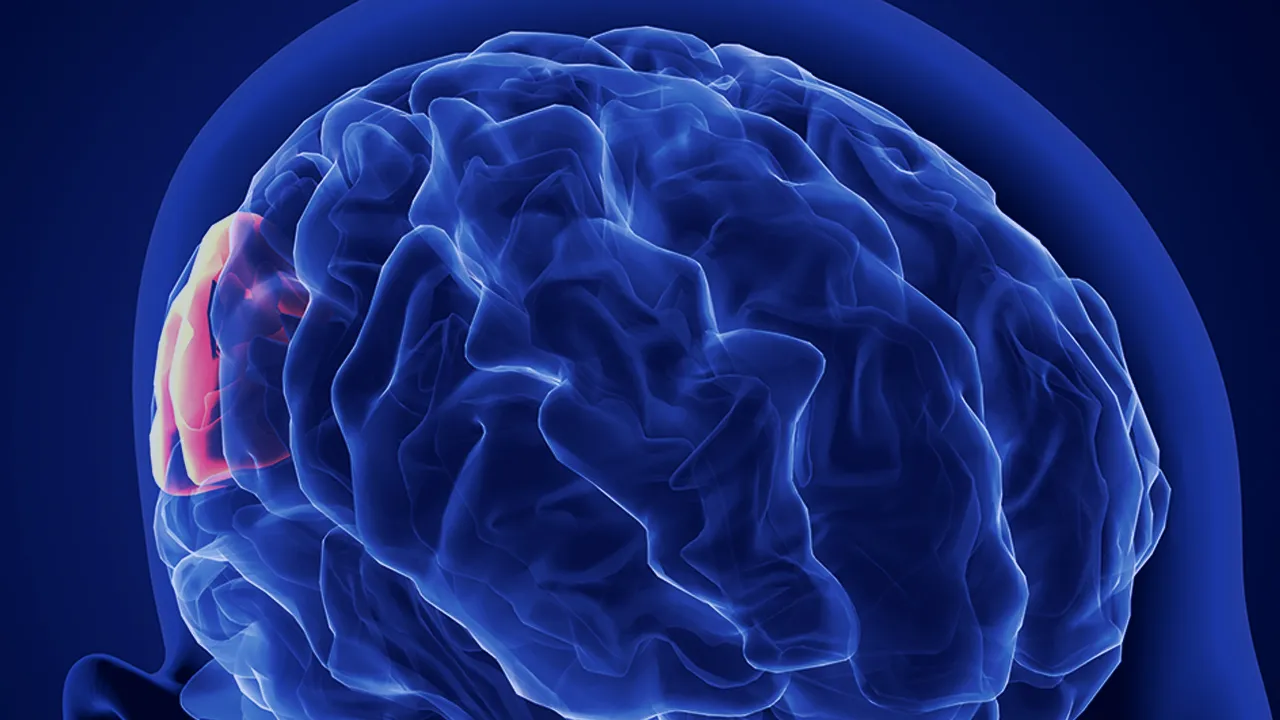
Understanding Ischemic Strokes: Recognizing Signs, Reducing Risks, and Recovering Strong
Ischemic strokes are a type of stroke that occurs when there is a blockage or obstruction in the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. This blockage can be caused by a blood clot or plaque buildup in the arteries, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the brain cells. Ischemic strokes are the most common, accounting for approximately 87% of all strokes.

Unmasking the Thief of Memories: Understanding and Combating Korsakoff’s Psychosis Syndrome
Korsakoff’s psychosis syndrome, also known as Korsakoff’s syndrome or Korsakoff’s disease, is a neurological disorder that results from a thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency. Causes This deficiency is often caused by chronic alcohol abuse, inhibiting the absorption of Thiamine and interfering with its metabolism. However, it can also be caused by other factors such as malnutrition, […]
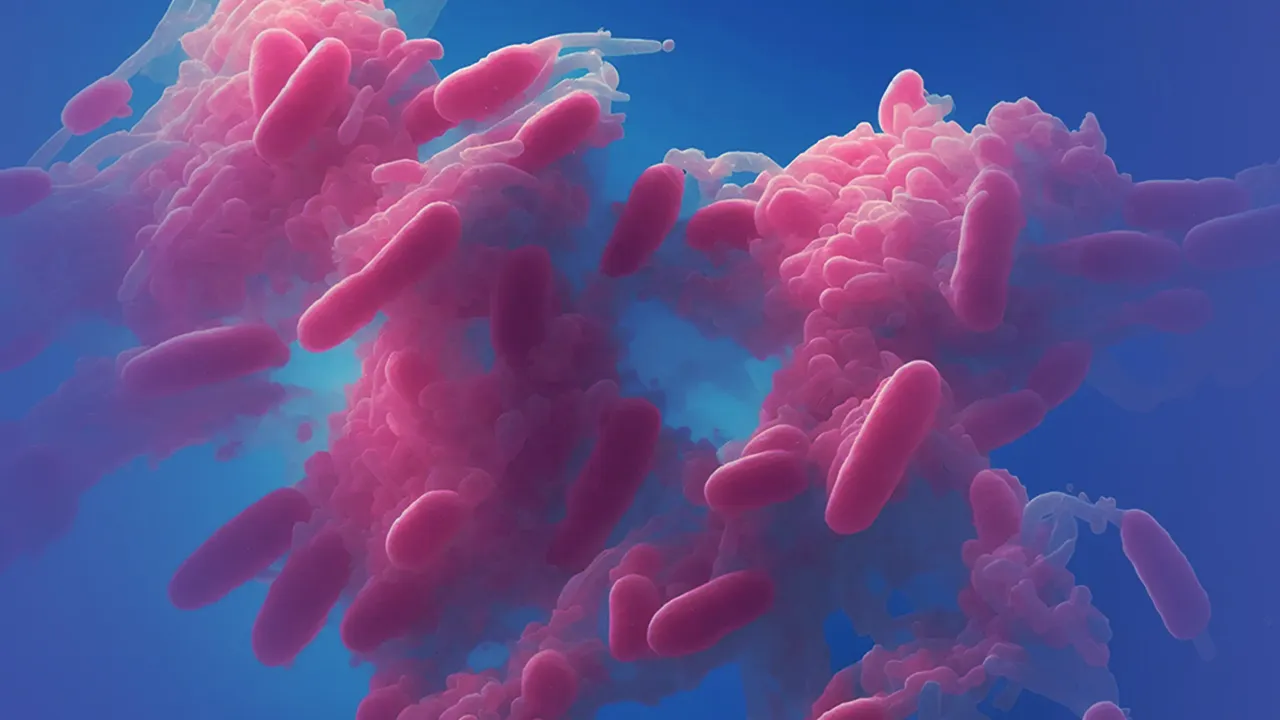

Botulism – Everything You Need to Know
Botulism is a rare but severe illness caused by a toxin produced by Clostridium botulinum. While it can affect people of all ages, infants are particularly susceptible, usually contracting the disease through contaminated food or spores present in diaper rash creams. The symptoms of botulism include difficulty breathing, blurred vision, weakness, and, in severe cases, […]

Down’s Syndrome: Everything You Need to Know
Introduction: Down’s syndrome is a genetic condition that affects approximately 1 in every 700 babies born in the United States. It is caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21, which leads to physical and intellectual disabilities. Despite the challenges of Down’s syndrome, individuals with this condition can lead fulfilling lives. Physical Characteristics of Down’s […]

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Introduction: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most severe type, affecting boys and young men who inherit the genetic defect responsible for the disease. It is characterized by progressive muscle weakness and loss of muscle mass and is typically fatal in early adulthood due to complications of muscle weakness and wasting. Causes of Duchenne Muscular […]

Drunkenness and Alcoholic Coma: What You Need to Know
Introduction: Drunkenness and alcoholic coma are two serious consequences of excessive alcohol consumption. While drunkenness is common, alcoholic coma is a rare but life-threatening condition resulting from prolonged and heavy drinking. While drunkenness is often associated with social drinking, it can also be a sign of alcohol abuse or addiction. In addition, chronic alcohol abuse […]
Dermatomyositis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Introduction: Dermatomyositis is a rare inflammatory disease that affects the muscles and skin. It is a type of autoimmune disease, meaning that it is caused by the body’s immune system attacking healthy cells or tissues instead of foreign substances like bacteria or viruses. Dermatomyositis can affect anyone but is more common in adults than children […]

Depression: What You Need to Know
Introduction: Depression is a mental health disorder affecting millions worldwide, yet it remains largely misunderstood and stigmatized. Definition: Depression is more than just feeling sad or down temporarily. It is a complex and persistent mental health condition characterized by a deep sense of hopelessness, loss of interest, and a range of physical and emotional symptoms. […]